Introduction
The three dimensional wind vector calculations are based on
the difference between the aircraft's air speed and ground speed. The
aircraft's air speed is determined using five pressure ports (Figure 1)
located on the nose of the aircraft. The Pitot Nose pressure is measured
using the center port, the attack angle is measured using the top and bottom
ports, and the sideslip angle is measured using the difference between the
two side ports. Bleed air from the engines is used to heat the radome
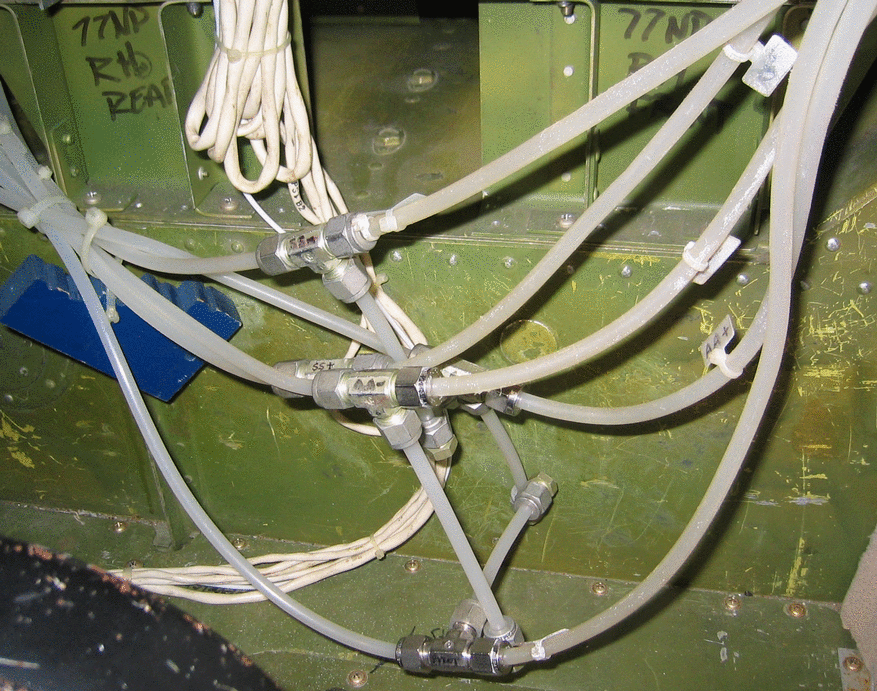
(Figure 2) to help prevent ice build which can block the ports. Tubes,
with water traps (Figure 3), connect each port to pressure transducer located
in the nose of the aircraft.
The aircraft's ground speed is determined using an Applanix Position and Orientation
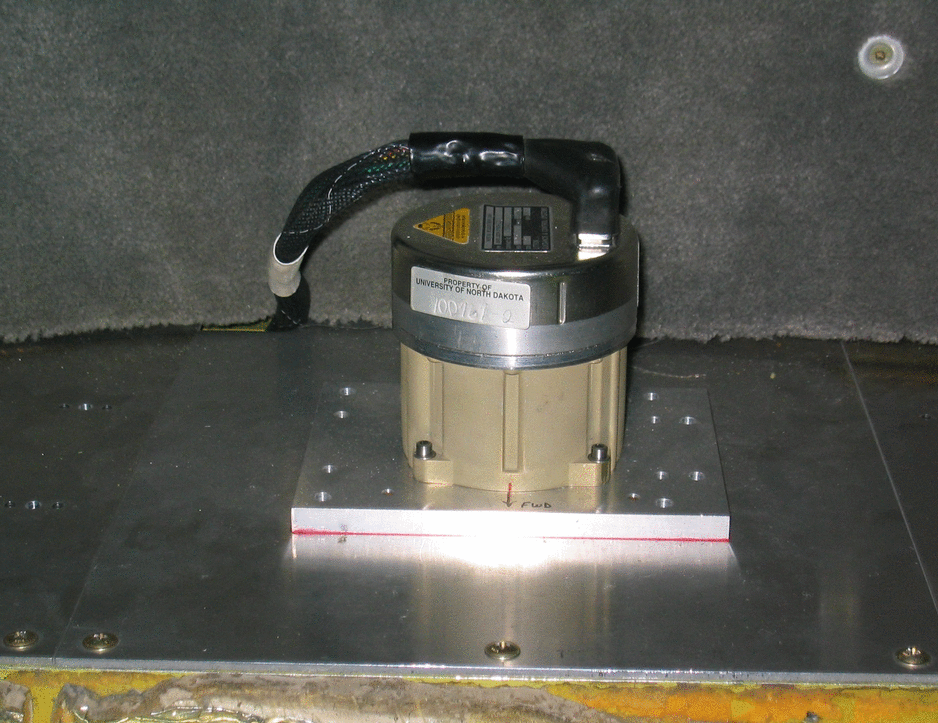
System (POS). The POS system consist of a Inertial Measurement Unit
(IMU) (Figure 4), GPS antenna, and the POS Computer System (Figure 5). The
POS system computes an optimally accurate navigation solution using both
inertial and GPS information. Real time 25 Hz data is received from
the POS unit during flight and is recorded along with the other instrument
data by the M200 data system. The POS data is also recorded at 200 Hz
on a flash memory card that can be removed from the POS system and post processed
to obtain a more accuracy navigation solution. The post processing procedure
uses a Kalman filter based integrated navigation algorithm to compute the
optimally accurate navigation solution.
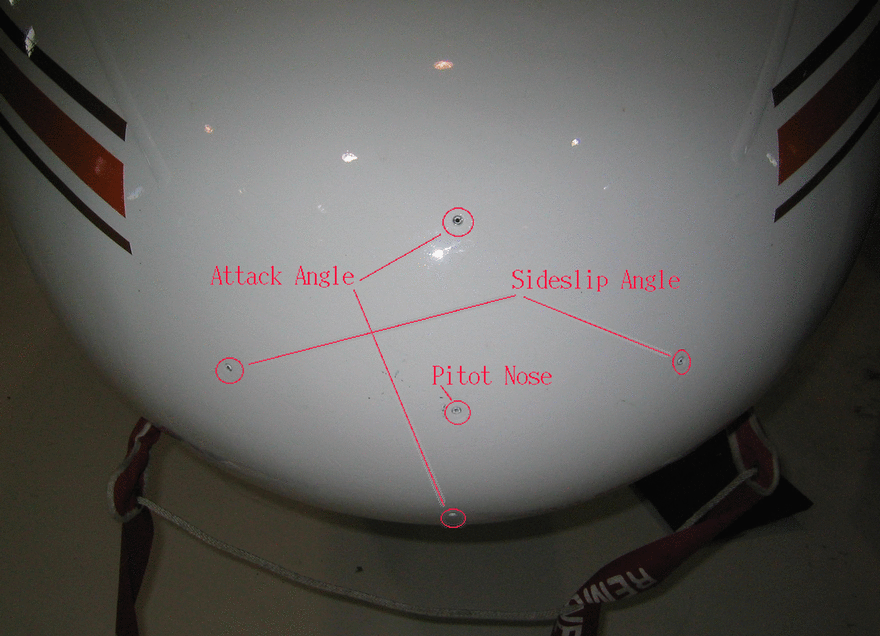
Figure 1: The nose of the University of North
Dakota's Citation aircraft showing the five pressure ports used to measure
the pitot nose pressure, the attack angle, and sideslip angle.
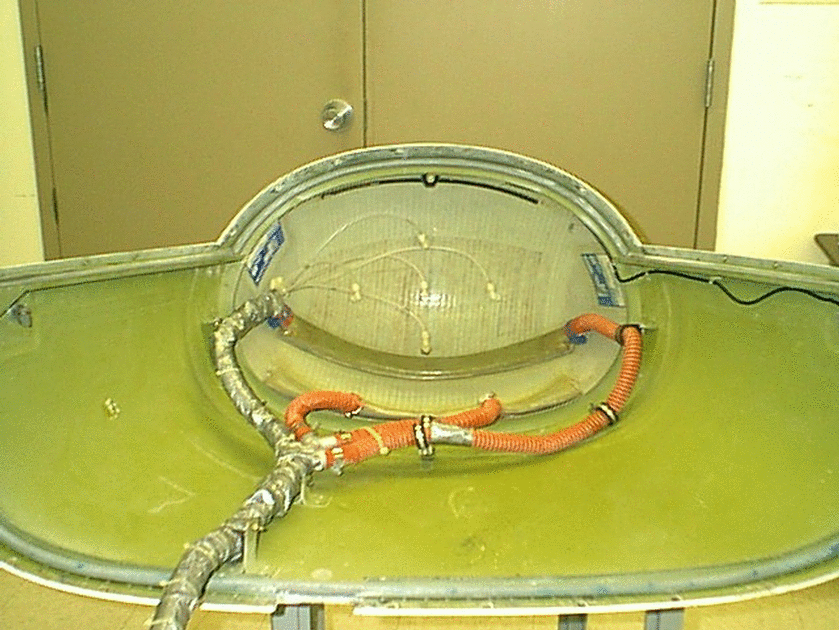
Figure 2: The inside of the radome of the University of North Dakota's
Citation aircraft showing tubes connected to the five pressure ports on the
Aircraft's nose.
Figure 3: The tubes and water traps in the
nose of the University of North Dakota's Citation aircraft.
Figure 4: The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
located in the back of Citation Aircraft cabin.
Figure 5: The Position and Orientation System
(POS) mounted in a 19" rack in the cabin of the University of North Dakota's
Citation aircraft.
Please contact David
Delene at delene@aero.und.edu
with your questions or comments.
Citation Aircraft Wind Calculation
Page