| The calibraton of the University of North Dakota's King Probe requires the determination of three calibration coefficients: C, x, and a. The first step is to create a plot of King Probe voltage versus true air speed. The best way to get the data for this plot is to take a dry run during a flight. During this run the plane must fly out of cloud and vary its airspeed, preferrably anywhere between 60 and 140 m/s, while maintaining a constant pressure altitude. After the data points for the plot are obtained the calibration program entitled "king_calib" is used to calculate the calibration coefficients. | The subroutine accepts arguments
passed from the command line that include the start and end times of the
calibration data during the flight, the analog file name, the winds file
name, and the physical file name for that flight. After the data
is read in by the program it uses a curve fit function to find the best
fit the data. The program fits a function of the from
|
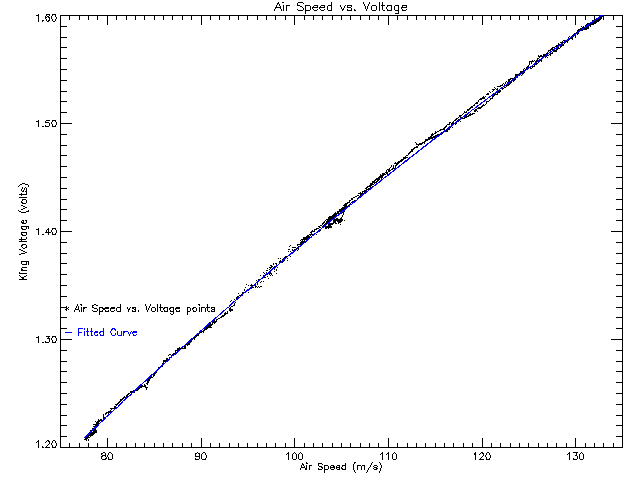
| The best fit curve for this data is:
|
Dividing through by 10 then yields:
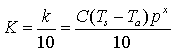 ,
(8) and ,
(8) and
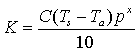 (10)
(10)
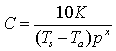 .
(11) .
(11) |
This calibration procedure should be done after any repair, change, or service to the instrument. Any work done to the instrument may greatly change the calibration coefficients. Also, the constants should be verified at the start and end of every field project. The values may not be exactly the same but it should be checked to see that any difference is negligable.